As threats in the digital realm evolve, the NIST Cyber security framework (CSF) 2.0 serves as a crucial resource to help businesses of all sizes, across industries to reinforce their defences against cyber security threats. This updated guidance focuses on a comprehensive set of standards, guidelines, and best practices and aims to streamline risk management and bolster information security frameworks [1].
The transformation from the original to the NIST CSF 2.0 illustrates a commitment to adapting to the shifting landscape of cyber threats, offering a meticulously curated toolkit that encompasses a NIST cyber security framework template for enhancing an organisation’s cyber security posture.
- CSF Core, Organisational Profiles, and Tiers:
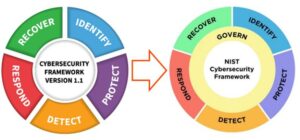
- CSF Core: Offers a set of cybersecurity activities and outcomes organised into six Functions: Govern, Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover, aiming to provide a high-level taxonomy to manage cybersecurity risks .
- Organisational Profiles: These profiles help in understanding an organisation’s current and target cybersecurity postures by mapping to the CSF Core’s outcomes, enabling a tailored approach to risk management [1].
- CSF Tiers: Describe the degree of formality and sophistication an organisation applies to cybersecurity risk management, reflecting its risk management practices [1].
- Resources for Implementation:
- The framework is supported by various resources including Informative References, the Cybersecurity & Privacy Reference Tool (CPRT), Implementation Examples, and the CSF 2.0 Reference Tool. These tools facilitate the application of the framework in real-world scenarios [1].
- Quick Start Guides (QSG) are available for different organisational needs such as Small Business (SMB), Creating and Using Organisational Profiles, and Using the CSF Tiers, among others, providing step-by-step guidance for different stakeholders[1].
- Adaptability and Scope:
- The CSF 2.0 is designed not as a one-size-fits-all solution but as a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risk. It caters to organisations of all sizes, across various industries, and at different stages of cybersecurity program maturity, underscoring its broad applicability and flexibility.
- The framework now includes a broader scope, addressing the modern cybersecurity landscape and contemporary threats, with a particular focus on governance and supply chains. This expansion ensures that the framework remains relevant and effective in the face of evolving cybersecurity challenges.
By providing a structured yet adaptable framework, the NIST CSF 2.0 aims to equip organisations with the tools and guidance necessary to enhance their cyber security measures effectively, reflecting the evolving nature of cyber threats and the need for comprehensive risk management strategies.
Key Updates and Enhancements in NIST CSF 2.0
Governance and Strategy Alignment
- Introduction of the ‘Govern’ Function: Aligns cybersecurity strategies with business objectives, ensuring significant roles for executive teams and boards in cybersecurity risk management [2]
- Tiered Approach to Cybersecurity Risk Management: Introduces tiers that characterise an organisation’s cybersecurity governance and management practices, ranging from ‘Partial’ to ‘Adaptive’, encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation based on risks from suppliers and services used.
Supply Chain and Continuous Improvement
- Emphasis on Supply Chain Security: Encourages entities to evaluate suppliers’ cybersecurity measures for a resilient ecosystem and introduces extensive supply chain flow-down requirements.
- Continuous, Quantitative Risk Assessment: Prioritises continuous improvement, strengthening supply chain risk management, and enhancing implementation examples. Automation and AI-based tools are highlighted for near real-time risk assessment.
Framework Structure and Resources
- Revised CSF Core: The new structure includes four Functions—Identify, Protect, Respond, and Recover—with the Detect Function integrated into the other Functions. It comprises 18 Categories and 72 Subcategories, providing a clearer and more actionable framework.
- New Resources and Tools: Introduction of Implementation Examples, Quick-Start Guides, and the CSF 2.0 Reference Tool, along with a searchable catalog of Informative References and the Cybersecurity and Privacy Reference Tool (CPRT). These resources aim to streamline the framework’s adoption and customisation based on organisational needs [2]
These enhancements signify NIST’s commitment to evolving the CSF in line with current and emerging cybersecurity threats, ensuring that organisations can leverage a tailored, flexible, and comprehensive framework to safeguard against cyber risks.
Impact on Organisations
The implementation and adaptation of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0 have far-reaching implications for organisations, influencing their approach to cybersecurity, compliance, and business operations. Here are key impacts:
- Adaptability and Efficiency:
- Not all controls outlined in the NIST CSF are necessary for every organisation, highlighting the framework’s adaptability to various business sizes and types [3]
- The Baldrige Cybersecurity Excellence Builder (BCEB) integrates with the NIST CSF to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of an organisation’s cybersecurity measures, ensuring that investments in cybersecurity yield tangible results [3]
- Compliance and Business Opportunities:
- By aligning with the NIST CSF 2.0, organisations can meet regulatory, contractual, and cyber insurance requirements more efficiently, positioning them favorably in the eyes of regulators and partners.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs) face new challenges and opportunities with the CSF 2.0’s emphasis on governance and Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management. This scrutiny from clients can lead MSPs to offer additional compliance services, creating new revenue streams [3]
- Continuous Improvement and Vendor Scrutiny:
- The framework encourages a culture of continuous improvement, especially in supply chain security. Organisations are prompted to assess their suppliers’ cybersecurity practices closely, fostering a more secure and resilient ecosystem [3]
Conclusion
Through this exploration of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework 2.0, we’ve underscored its significance in fostering a more adaptable, robust, and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity risk management. The key updates and enhancements, from the introduction of the ‘Govern’ function to the emphasis on supply chain security, illustrate a strategic realignment that resonates with the contemporary cybersecurity landscape. Moreover, the framework’s potential to streamline compliance, enhance operational efficiency, and open avenues for continuous improvement has been highlighted as instrumental for organisations navigating the tumultuous waters of cyber threats.
As organisations grapple with evolving digital threats, the adoption of NIST CSF 2.0 emerges as a critical step toward fortifying cybersecurity postures. The framework not only offers a blueprint for resilient cybersecurity strategies but also aligns with business objectives, reinforcing the importance of cybersecurity in the broader context of organisational success. For those transitioning from NIST CSF 1.1 or contemplating the implementation of these frameworks, our experts at AMARU are here to provide guidance and support, ensuring a seamless transition. Embracing NIST CSF 2.0 represents a proactive stance in the ongoing battle against cyber threats, underscoring its centrality to modern cybersecurity endeavors.
References:
[1] https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/CSWP/NIST.CSWP.29.pdf
[2] https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2023/08/nist-drafts-major-update-its-widely-used-cybersecurity-framework
[3] https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2023/08/nist-drafts-major-update-its-widely-used-cybersecurity-framework


